On top of that, an outdated router firmware configuration and corrupted network data on your computer can also contribute to a slow internet speed. But whatever the cause may be, resetting your network settings, clearing up the piled-up cache files, and updating your router firmware can fix this issue for you. But there are a ton of other working fixes that will definitely work towards fixing the network issue. And we are going to talk about those methods here in this article.
Why is My Internet So Slow on Mac?
How to Fix a Slow Internet on a Mac?
The first thing to do when the internet is slow on your computer is to restart your system. This will discard an OS-related glitch that might have interfered with your workflow. Also, switch your browser and see if this internet issue still persists. However, if this doesn’t do much, follow the steps listed below.
Run Ping Test
A ping test is done to test the time data packets take to move from the client to the host device. So, it’s important to determine if you’re actually receiving these data packets from your ISP.
Restart Your Router
A simple way to counter your slow internet issue is to restart your router. Doing so will refresh your network connection status by grabbing a new signal from your ISP. This will fix your slow internet issues as well as other basic network-related problems.
Position Your Router in a Suitable Environment
The position of your router greatly determines the network signal you receive. Placing it near electronic devices can cause network interference, disrupting the signal and slowing down the connection. That’s because electronic devices generally use a 2.4GHz channel, the same as what your Wi-Fi usually relies on. Also, if you have a dual-band router, we recommend that you switch your connection to a 5 GHz band to improve your internet speed. However, the 5GHz band doesn’t cover a large area. Hence, for a better network experience, it is best to stay close to your router. Also, we recommend you avoid placing your router near walls or directly on the floor as they might absorb the Wi-Fi signal and disrupt your network experience. So, if possible, look for an open area to position your router on.
Forget and Reconnect Your Wi-Fi
To remove any wireless network issues, you can ‘Forget’ your Wi-Fi settings and reconnect to it again. Doing this will delete your network information, such as your password, from the computer. The particular network will also be cleared from your system’s Saved Network List. However, the next time you try to connect to this network, your system will ask you to re-enter your password. This fresh network signal can fix your slow internet issue.
Diagnose Your Network With the Wireless Diagnostics Tool
The wireless diagnostics tool is the macOS’s network troubleshooter that aims to find issues within your Wi-Fi network. It first scans this network, and if there are any signs of error, it pinpoints the exact issue and helps you fix it. Here’s how you run the Wireless diagnostics tool:
Switch to Ethernet Cable
Wired connections are significantly faster than wireless connections. For starters, a wired connection provides a dedicated bandwidth for you, one which only you can operate upon. On the contrary, when you connect to Wi-Fi, you have to share the total bandwidth with all the other users on the network. Although most Macs these days don’t have the traditional ethernet port on them, you can still use USB hubs that have a dedicated ethernet port. If you usually face internet issues, then switching to an ethernet cable will be a favorable move for you.
Delete the Network Properties Files
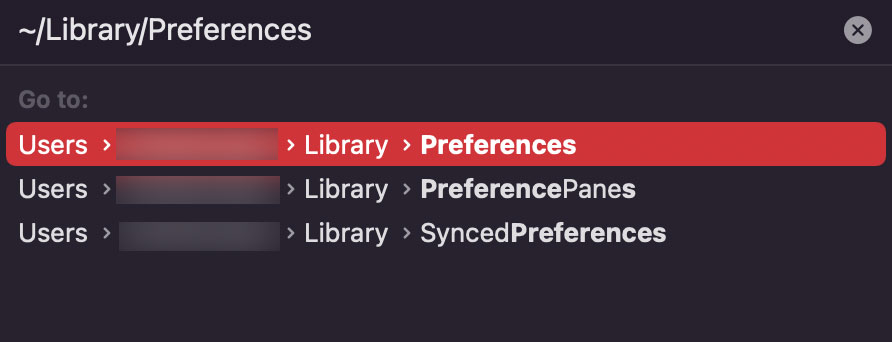
There is no exact method to reset the network settings on your Mac. There is, however, a workaround to this. That is where the network properties files come into play. These properties files contain your profile information and configuration settings. Hence, deleting these files will mimic a network reset as all the information present within them is cleared up. Deleting the .plist files are safe and also recommended, as they will automatically regenerate the next time you connect to the internet. These files reside in the Preferences folder, and here’s how you get to them:
Close Background Apps
Background applications can also result in a slow internet connection. Moreover, if an application working in the background is using the internet to upload/download certain data, it can undoubtedly hamper your overall network experience. So, if any unnecessary applications are running in the background, we recommend you close them and see where that takes you. Here’s you do so:
Clear Browser Cache
Your browser automatically generates cache files and stores them on your computer. These cache files are meant to load up your browser profile and websites faster. However, the more you use that particular browser, the more cache files tend to pile up. This will then start to cause network performance issues, and clearing the cache from time to time will fix and prevent any forthcoming slow internet problems. On Chrome On Firefox On Safari
Scan for Viruses
Malware and viruses present on your computer can also cause network lags and issues. Usually, files downloaded from unreliable third-party sites often lead to virus infection. And if your system is a victim of a large virus outbreak, this can severely slow down your internet, along with other system compatibility and stability problems as well. So, we recommend you invest in good antivirus software and scan your computer for any signs of such attacks. If malware is found on your system, deleting the infected application/file could fix your internet problem.
Disable VPN and Proxy Server
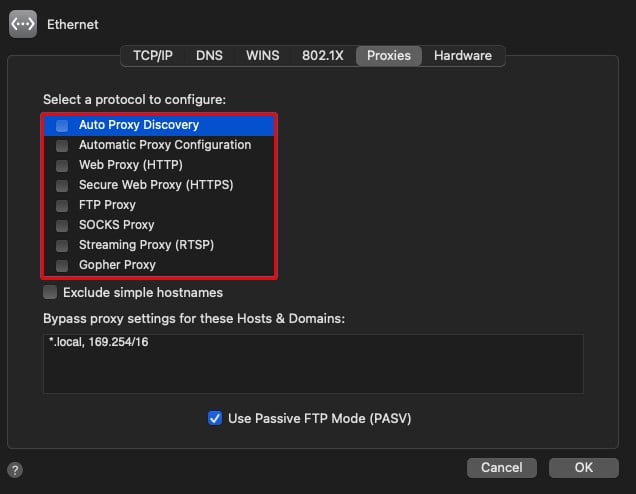
VPNs and Proxy servers are meant to maintain your online anonymity. However, they do interfere with the network connection from time to time. They also significantly slow down your internet connection. So, if you have VPN enabled on your system, we recommend that you turn it off. The same goes for proxy servers. However, the proxies can be disabled directly from your browser, and here are the steps to do so:
Start Quality of Service (QoS)
The Quality of Service feature on your router is useful to make way for important data packets to travel through the network. It allows you to prioritize the network bandwidth with uplink and downlink i.e., you can manually set the upload and download speed depending on the task at hand. For example, if you’re downloading data through the network or streaming some content online, you can prioritize downlink QoS over the uplink. On the contrary, if you’re uploading your data on the internet, you can prioritize uplink QoS to improve your network experience. Furthermore, setting an unsuitable QoS over what’s really needed can also slow down your internet speed. So, enabling the right QoS ensures that the network traffic flows without congestion and makes sure that one device is not hogging up the bandwidth.
Update Your Router Firmware
Updating your router firmware incorporates new security patches for your online experience. It will also fix technical bugs and glitches that repeatedly interfere with your network signal. You can update your router firmware by visiting the router settings page, and here’s how you do it: However, if you cannot automatically check for the latest firmware updates or if no download links are given on the router settings page, visit your device manufacturer’s website. Search for your router model and download the latest firmware from there.
Update macOS
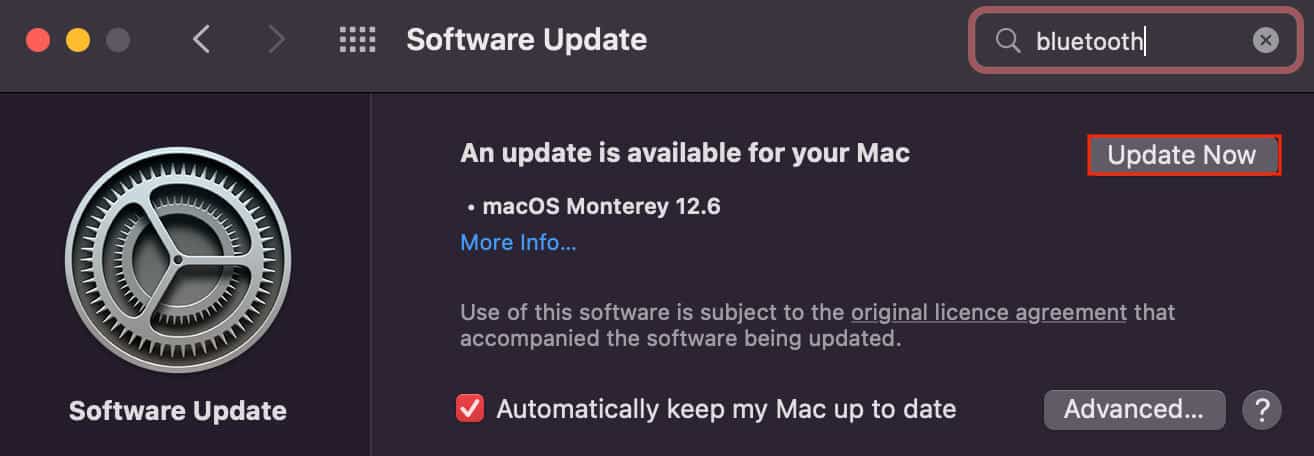
Apple releases new system software upgrades in a timely manner. This is done to overcome any compatibility issues and stability problems on your computer. So, if a new software update is available or if you have a ton of updates piled up on your computer, we recommend you update the macOS as fast as possible.